

This getting started guide shows how to install Jbi4EJB and a sample service assembly in OpenESB, using the Jbi4EJB component. Notice that this component is tested also with Servicemix 3.1.
A binding component using Jbi4Ejb exposes on the internal BUS an external service provided by a stateless session EJB. The EJB must be deployed on an Application Server and be reachable through a corbaname (according to the requirements). In the following sample we use OpenESB (included in Glassfish v2).
Thus the integration scenario is shown in the following figure:
Install the Netbeans 5.5 or the Netbeans 6.0 (or newer) IDE and the NetBeans Enterprise Pack. When installing the Enterprise Pack, select to install also the Sun Java System Application Server 9 (that contains OpenESB).
Download the Jbi4Ejb component. Install and start the component using the contextual menu on the server JBI module.
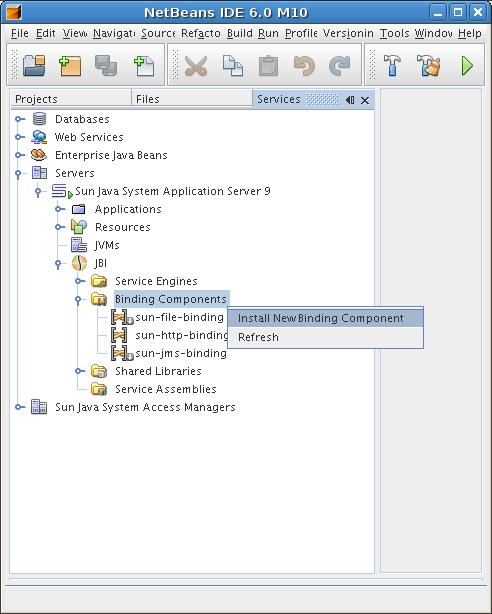
After these operations if the compoenet is correctly started, you can deploy a Service Assembly that uses the Jbi4Ejb component.
A service assembly is a deployable item that configures one or more endpoint inside a JBI ESB. We are going set up a configuration that take an EJB service and expose it a SOAP/HTTP Webservice. The configuration is shown in the following figure:
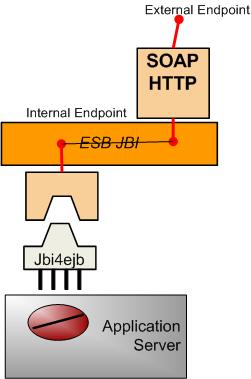
The Jbi4Ejb component creates an internal (i.e. visible inside the ESB) endpoint. This internal endpoint is exposed as an external endpoint with the Http-Soap Binding Component. The http component will proxy the incoming externall calls to the internal endpoint exploiting the JBI routing mechanisms.
A Service Assembly (SA) is a zip file containing one or more Service Unit (SU) file, each Service Unit defining one or more endpoint. We need two endpoint so we're going to configure two SUs:
A Jbi4Ejb service unit must have the layout:
+- <SERVICE_WSDL.wsdl>
+- META-INF/
+- jbi.xml
where:
The SERVICE_WSDL.wsdl can be generated using the Netbeans plug-in or the command-line tool. This WSDL is extended using the Jbi4Ejb extensions (see the WSDL Extensions guide for the details) which express:
For example, the WSDL can have this form:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<wsdl:definitions targetNamespace="http://complex.test14.imolinfo.it"
xmlns:tns="http://complex.test14.imolinfo.it"
xmlns:imolaejb="uri://schemas.imola.it/jbi/wsdl-extensions/ejb/"
(...)
<wsdl:types>
(...)
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:message name="getUserProfileResponse">
(...)
</wsdl:message>
<wsdl:portType name="<SERVICE_INTERFACE>">
(...)
</wsdl:portType>
<wsdl:binding name="TestComplexSessionRemoteBinding" type="tns:TestComplexSessionRemote">
<imolaejb:binding>
<imolaejb:orb>
<imolaejb:property name="org.omg.CORBA.ORBClass" value="com.ibm.CORBA.iiop.ORB"/>
</imolaejb:orb>
</imolaejb:binding>
(...)
</wsdl:binding>
<wsdl:service name="<SERVICE_NAME>">
<wsdl:port name="<ENDPOINT_NAME>" binding="tns:TestComplexSessionRemoteBinding">
<imolaejb:address name="corbaname:iiop:127.0.0.1:2809/NameServiceServerRoot#ejb/TestComplexSessionBean"
localizationType="corbaname"/>
</wsdl:port>
</wsdl:service>
<imolaejb:types>
<imolaejb:serialVersionUID className="it.imolinfo.test14.complex.UserProfile" UID="8891581763048162223"/>
<imolaejb:serialVersionUID className="it.imolinfo.test14.complex.UserProfileException" UID="-5706164759540452783"/>
</imolaejb:types>
</wsdl:definitions>
The jbi.xml must have the following content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><jbi xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jbi" version="1.0">
<services xmlns:jbi4corba-test="<SERVICE_NAMESPACE>"
<provides
endpoint-name="<ENDPOINT_NAME>"
interface-name="ns1:<SERVICE_INTERFACE>"
service-name="ns1:<SERVICE_NAME>"/>
</services>
</jbi>
This configuration specify that the Service Unit is a Binding Component.
Zip all the files in the specified layout and name the archive Jbi4EjbSU.zip.
A http service unit using the OpenESB http soap binding component (named sun-http-binding in the open-jbi-components bundled with Netbeans 6) must have the following layout:
+- <SERVICE_WSDL.wsdl>
+- META-INF/
+- jbi.xml
where:
the jbi.xml has the following content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<jbi xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jbi"
xmlns:ns1="<SERVICE_NAMESPACE>" version="1.0">
<services binding-component="true">
<consumes
endpoint-name="<ENDPOINT_NAME>"
interface-name="ns1:<SERVICE_INTERFACE>"
service-name="ns1:<SERVICE_NAME>"/>
</services>
</jbi>
where:
Zip all the files in the specified layout and name the archive HttpSU.zip.
The service assembly is unit of deployable configuration in JBI, in our example it has the following layout:
+- Jbi4EjbSU.zip
+- HttpSU.zip
+- META-INF/
+- jbi.xml
where:
The jbi.xml has the following format as described in the JBI Specification:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<jbi xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jbi" version="1.0">
<service-assembly>
<identification>
<name><SA_NAME></name>
<description><SA_DESCRIPTION></description>
</identification>
<service-unit>
<identification>
<name><SU1_NAME></name>
<description><SU1_DESCRIPTION></description>
</identification>
<target>
<artifacts-zip>Jbi4EjbSU.zip</artifacts-zip>
<component-name>Jbi4Ejb</component-name>
</target>
</service-unit>
<service-unit>
<identification>
<name><SU2_NAME></name>
<description><SU2_DESCRIPTION></description>
</identification>
<target>
<artifacts-zip>HttpSU.zip</artifacts-zip>
<component-name>SUN-HTTP-BINDING</component-name>
</target>
</service-unit>
</service-assembly>
</jbi>
where:
Notice that the BC filenames (Jbi4EjbSU.zip and HttpSU.zip) are specified with the respective component (Jbi4Ejb and SUN-HTTP-BINDING). Zip all the files in the specified layout and name the archive HttpToEJBSA.zip (the archive name is not important).
In NetBeans, with the server started, select from "Service Assemblies" the "Deploy New Service Assembly" option.

If the Service assembly is correctly deployed, then you can start it. When the SA is starting, the EJB referred must be reacheable. If this is not true, the SA start fails.
If the Service Assembly starts correctly, you should see both the SU running
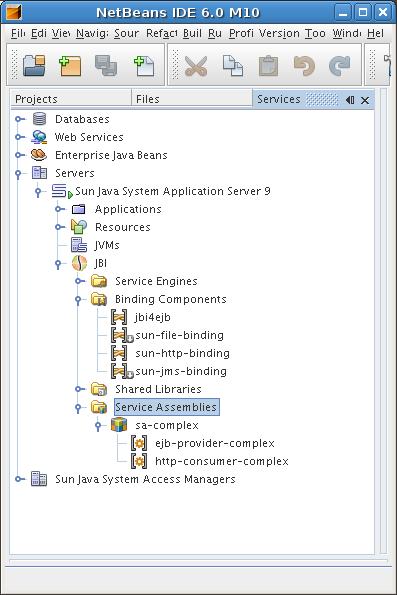
Now you can test the service assembly sending a SOAP message to the HTTP endpoind (the service address is specified in the SERVICE_WSDL.wsdl description inside the HttpSU.zip).